SEO title tags are small but mighty. Though only 55 to 70 characters long, they are very important.
If you view writing page title tags as just another task to complete before publishing SEO content, you’re missing a significant opportunity to attract more organic traffic and enhance your website’s SEO.
What Are SEO Title Tags?
An SEO title tag is an HTML element that assigns a descriptive name to a web page. Also referred to as a meta title or page title, title tags identify a page in external locations such as search engine results pages (SERPs), social media posts, and browser tabs.
Web pages must have distinct and unique title tags.
Why Are Title Tags Important?
A well-crafted title tag is crucial for:
- Ranking in Search Engines: SEO title tags play a significant role in how Google and other search engines understand the content of a page. By incorporating relevant keywords, title tags help search engines match your page to user queries, thereby improving search rankings.
- Driving Clicks: An effective SEO title tag entices readers to click through to a page from organic search results or social media links. It captures attention and convinces users that your content is valuable, interesting, and precisely what they need.
- Helping Users Keep Track of the Page: Title tags also appear in browser tabs and bookmarks – which allows users to easily identify and return to your page.
Title Tags Vs. H1 Tags: Understanding the Distinction
While both title tags and H1 headings play essential roles in web optimisation, they serve distinct purposes and appear in different locations.
Title Tags: Off-Site Visibility
SEO title tags act as your webpage’s identity in off-site locations, such as SERPs and browser tabs. They provide users with a concise preview of your content, influencing their decision to click and visit your page. Title tags should (and by should I mean must) be clear, descriptive, and optimised for relevant keywords.
H1 Headings: On-Site Structure
H1 headings, on the other hand, function primarily on the webpage itself. They represent the main heading or title of your content, serving as a visual hierarchy for your readers. H1 headings structure your content and enhance readability by conveying the central theme of your page.
Leveraging the Power of Both
While both elements can (and often do) contain similar keywords, it’s generally recommended to differentiate them slightly. This allows you to:
- Optimise Title Tags for Search: Title tags can be crafted with a call to action or incorporate additional keywords to enhance search engine visibility.
- Prioritise User Experience: H1 headings can be phrased more naturally for readers, focusing on clarity and conciseness within the context of your content.
Example: A Balancing Act
Consider this example from The Balance’s article on small business marketing:
- H1 Heading: “Marketing Basics for a Small Business” (Clear and concise, conveying the page’s main topic.)

- Title Tag: “Learn Marketing Basics for a Small Business” (Slightly different, using “learn” as a call to action and potentially improving click-through rates in search results.)

By understanding the distinct roles of title tags and H1 headings, you can leverage them effectively to enhance both your SEO efforts and user experience.
Where Do Title Tags Appear?
While SERPs are a primary consideration for SEO title tags, their reach extends far beyond. Here’s a breakdown of where these essential elements appear:
Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs):
This is a familiar territory. SEO title tags function as the clickable headline displayed between a page’s URL and meta description in SERPs. They significantly influence user click-through rates – a compelling and informative title tag motivates users to visit your page.
While your written title tag is typically used, there may be instances where Google generates its own based on its understanding of your content.
Browser Tabs
The title tag will always come to the rescue when you’re juggling too many open tabs. it appears on the browser tab as the name of the page you’re currently viewing. This allows users to easily identify and navigate between open tabs.
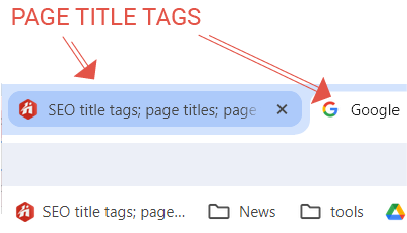
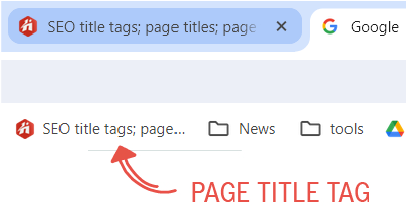
Bookmarks
Ever bookmarked a valuable resource? The page title becomes the default name of that bookmark. A descriptive and brand-inclusive title tag helps users to swiftly locate your bookmarked page for future reference.
Social Media Posts
Sharing a web link on social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter often results in the platform turning the URL into a clickable snippet with a title and description. This title is typically derived from the page’s title tag, providing a glimpse into your content and encouraging clicks.
External Websites
External websites may link to your page using your title tag as the anchor text. This reinforces the importance of writing an SEO title tag that accurately represents your page’s content and therefore improves user understanding and navigation.
How to Write Page Titles For SEO: A 5-Step Guide
While some flexibility exists, most effective SEO title tags follow this format:
- Article Title/Product Name | Brand Name
Remember, a great SEO title tag acts as a concise summary of your page content which has cater to both search engines and users.
SEO Essentials for Title Tag Optimisation
Integrate Your Target Keywords
Search engines leverage title tags to determine content relevance to user queries. Include your primary or a long-tail keyword variation at the beginning of the title, and for local businesses, consider incorporating your city or state. However, prioritise natural language – avoid keyword stuffing that comes across as spammy and hinders user experience.
Be Clear & Descriptive
Strive for page titles that are both clear and concise. You want users skimming SERPs to instantly determine if your content aligns with their search intent. This may involve making crucial decisions about which link to click.
Example:
A search for “weight training for women” yields these informative titles:
- Strength Training for Beginners | A Complete Guide
- 4-Week Weight Training Plan for Women – Shape Magazine
- 7 Best Strength Training Exercises for Women (Video)
These page titles effectively communicate what users can expect, which, in turn, is going to enable them to choose based on their needs – whether a few key exercises, a personalised plan, or general knowledge about strength training.
Place Your Brand at the End of the Tag
While keywords deserve the lead role, consider including your brand name towards the end of the title tag, separated by a hyphen or vertical slash (|) for improved readability. This practice helps users identify the domain they’ll be directed to, especially valuable for content shared on social media or bookmarks. Established brands leverage title tags to solidify brand recognition, while new businesses can build awareness through the same strategy.
Optimise the Length of the Title
To ensure complete title display in SERPs, aim for a character count between 55 and 70. Remember, wider characters consume more pixels. Titles exceeding 600 pixels will be truncated with an ellipsis (…). Check out my recommended free and paid SEO title checker tools to help you.
Optimise Your Page Titles for Click-Through Rates
Within the limited character space of SERPs, your title tag needs to convince users of your content’s value. Here are some strategies to maximise click-throughs:
- Content Depth: Indicate whether your content provides an in-depth analysis or a quick overview. Utilise phrases like “A Complete Guide to…” or “4 Easy Steps to…”
- Answering User Queries: Add keywords like “why,” “how,” and “when” to demonstrate your SEO content addresses user questions. For instance, “Where to Find the Best Bagels in Sydney, CBD.”
- Highlighting Selling Points: Use phrases like “best selection,” “free shipping,” or “free trial” to demonstrate your product’s or service’s benefits.
- Call to Action: Craft titles that motivate users to take action, such as “Shop Handcrafted Wooden Toys” or “Find a Dentist in Manchester.”
- Content Freshness: For recently updated content, incorporate a date in the title tag to convey fresh information to users. For example, “Best Meditation Apps for 2024.”
- Content Type Identification: Clearly denote content types like infographics or videos using brackets, enhancing readability. For instance, “How to Write a Cover Letter (with Downloadable Template).”
Pro Tip: Long-tail keywords help Google match your content to the right search intent.
For example, a blog post targeting “title tag” might use “How to Write Title Tags” to capture users seeking actionable how-to instructions.
Remember, Google’s sophisticated algorithms can grasp user intent. For instance, a search for “best U.S. national parks” may display titles that don’t explicitly use “best.”
- America’s 20 Most Popular National Parks, Ranked – Thrillist
- The Top 25 National Parks in America – Travel + Leisure
- 25 Top-Rated National Parks in the USA | PlanetWare
These titles don’t all include the word “best,” yet they effectively meet the search intent.
Common Title Tag Pitfalls to Avoid for On-Page SEO Success
While crafting title tags, even the most meticulous marketer can make mistakes. Here’s a breakdown of common pitfalls to steer clear of, alongside the SEO best practices outlined earlier:
1. Lack of Descriptiveness
A title tag simply labelled “Home Page” offers little value. For users, it fails to convey the essence of your business. A better approach, for instance, might be “Professional Landscaping Services in Melbourne” for a lawn care company.
2. Relevance Mismatch
Search engines favour title tags that accurately reflect a page’s content. A title like “Buying a New Home” might not precisely match a page focused on securing a mortgage. This is a missed opportunity to target a more relevant keyword, such as “How to Find a Mortgage for Your New Home.”
3. Duplicate Title Tag Usage
Each webpage requires a unique title tag to target specific keywords and signal to search engines that content is distinct. Duplicate titles create confusion, while unique titles enhance page differentiation. For example, an e-commerce store selling home decor should avoid using “Floral Wall Art” for multiple product pages. A more specific page title like “Framed Yellow Poppies Canvas Wall Art” is more effective.
4. Outdated Content
Maintaining up-to-date SEO title tags is necessary. If you included “2021” in a title tag last year to signify current information, it appears outdated in 2024.
Pro Tip for Evergreen Content: Regularly updating time-sensitive content allows you to maintain a long-standing URL with enduring freshness. Considering that the average top-ranking page boasts a lifespan of three years, prioritising an evergreen URL with frequent content updates presents a significant advantage.
Why Is Google Rewriting My Original Title?
Ever meticulously craft a title tag, only to see a different title displayed in search results? Here’s the deal:
Google uses a number of different sources to automatically determine the title link, but you can indicate your preferences by following our guidelines for writing descriptive <title> elements.”
They consider more than just your title tag, including:
- H1 and Other Headings: These headings can influence the title displayed in SERPs.
- Content Prominence: Content emphasised through stylistic elements can also play a role.
- Internal Anchor Text: This refers to the text used to link to your page within your website.
- External Backlink Anchor Text: This is the text used to link to your page from other websites.
Beyond Best Practices:
The common perception is that Google rewrites titles solely due to non-compliance with best practices. While that can be a factor, it’s not the entire story.
At the end of the day, Google reserves the right to select any element it deems most suitable for the title in SERPs, prioritising user experience. This rationale makes perfect sense – Google strives to deliver the most relevant and informative results for user queries.
Although there’s no guaranteed method to predict when Google rewrites titles, here are a few pointers:
- Monitor Industry Trends: Keep an eye on your industry’s SERPs to identify any emerging patterns in title selection.
- Experimentation is Key: Test different approaches to see what resonates with Google and your audience.
- Focus on Value, Not Control: While influencing the displayed title tag is desirable, it’s crucial to prioritise user value, because…
When Google tweaks the title to enhance user experience, it ultimately benefits your website.
As a precaution, make sure your primary keyword is included in both your title tag and H1 to help the page appear in relevant searches, including long-tail keywords to target user intent. Then, allow Google to refine the tag as necessary to focus the title and attract users.
Helpful Tools to Check Your Titles
Writing compelling SEO title tags is an important task, and fortunately, several tools can streamline the process:
- Mangool’s Google Search Simulator – a personal favourite
- Search Wilderness
- Capitalize My Title
- Comprehensive SEO tools like SEMrush and WordPress plugins such as Yoast also include built-in SEO title checkers as part of their optimization features.
If you’re ready to optimise your title tags, start with a comprehensive site audit.
My preferred tool is Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider, which provides an overview of how any meta tag is used on your site. This tool makes it easy to identify missing titles, duplicate title tags, and overly long tags, enabling you to apply these SEO tips and optimise them for search.
This tutorial guides you through using Screaming Frog to audit your H1 tags. You can follow the same steps to audit other on-page SEO elements, such as title tags.
Frequently Asked Questions About Title Tags
How do I write Title Tag HTML?
Most Content Management Systems (CMS) offer user-friendly forms for entering title tags and meta descriptions. These systems then automatically generate the HTML title tag.
However, if you want to directly incorporate the title tag within an HTML file, use <title> and </title> tags:
Example:
HTML
<title>Optimised Title Goes Here | Your Company</title>
Crucially, ensure the title tag resides within the HTML document header:
HTML
<head>
<title>Optimised Title Goes Here | Your Company</title>
</head>
How Long Should a Title Tag Be?
SEO experts generally recommend keeping titles between 55 and 70 characters to guarantee complete display in search results. It’s important to note that this isn’t a strict rule, but rather an industry standard practice.
While having an optimised title tag fit neatly within a search snippet promotes a professional appearance and prevents users from missing crucial information, Google’s search algorithms will still process longer titles for SEO purposes, even if the entirety of the tag isn’t shown in SERPs. Conversely, titles can be shorter than 50 characters if they effectively convey meaning to both search engines and users.
Can My H1 Tag and Title Tag Be the Same?
There’s no SEO penalty for having identical H1 and title tags. However, it’s generally not recommended to have these elements mirror each other exactly.
Reasoning: H1 tags and title tags, while both contributing valuable relevancy signals for SEO, serve distinct functions for searchers and website visitors. By keeping them the same, you miss the opportunity to fully optimise each element for its intended purpose.
SEO Title Tags: Key Insights
You now have the essential knowledge to write effective meta tags for your titles. Here’s a concise summary of what you should keep in mind when writing page titles to enhance online visibility and increase click-through rates to your website:
- A title tag, also referred to as a page title, is an integral part of a website’s HTML code.
- SEO title tags communicate to both users and search engines what the webpage is about.
- Unlike h1 headers that appear directly on a page, title tags display in search results pages, browser tabs, bookmarks, and social media shares.
- Incorporate your primary keyword or a relevant long-tail version early in the title.
- If including a brand name, position it at the end of the title using a separator like a hyphen or vertical slash ( | ).
- Page title tags should be descriptive and compelling to encourage users to click through.
- To achieve optimal ranking, be sure to write titles that accurately reflect the content of your pages.
- Aim for a length of 55-70 characters to prevent truncation in search engine results pages.
- Use tools to preview your title tags before finalising them.
- Conduct a site audit to identify missing titles, check title tag lengths, and incorporate terms based on your keyword research.
Ready to Leverage the SEO Power of Page Titles?
Page titles may seem like a small part of SEO, but they cast a large shadow… after all, there’s only one on every page of your site! Hawk SEO can audit your SEO title tags and optimise them to improve your ranking and click-through rates to help you achieve your digital marketing goals. Schedule a free consultation with our SEO specialists today and learn more.




